Tuesday, 16 January 2018
Wednesday, 10 January 2018
Demo: Interface Policies
Create Link Level Policy:
Create CDP Interface Policy
Create LLDP Interface Policy
Create Port Channel Policy
MCP Interface Policy
Tuesday, 9 January 2018
Demo: OOB Mgmt Policies
Monday, 8 January 2018
Demo: Creating a Tenant
Topology
Tenants > Add
By default you have Common / Infra / Mgmt
Create Tenant Brisbane
Create Tenant Sydney
Demo: Fabric Discover Process
Credits to Mr. Lunde.
Fabric > Fabric Membership
Here, the process of LLDP, COOP (Council of Oracle Protocol) takes place...
Fabric > Fabric Membership
Here, the process of LLDP, COOP (Council of Oracle Protocol) takes place...
Thursday, 4 January 2018
ACI: Configuring a SPAN Session
(This is from ACI Built in Help)
This procedure shows how to configure a SPAN policy to forward replicated source packets to a remote traffic analyzer.
- In the menu bar, click Tenants.
- In the submenu bar, click the tenant that contains the source endpoint.
- In the Navigation pane, expand the tenant, expand Troubleshooting Policies, and expand SPAN.
- Under SPAN, right-click SPAN Destination Groups and choose Create SPAN Destination Group.The Create SPAN Destination Group dialog appears.
- Enter the appropriate values in the required fields of the Create SPAN Destination Group dialog box then click OK and Submit.Note:For a description of a field, click the information icon (i) at the top-right corner of the dialog box to display the help file.
- Under SPAN, right-click SPAN Source Groups and choose Create SPAN Source Group.The Create SPAN Source Group dialog appears.
- Enter the appropriate values in the required fields of the Create SPAN Source Group dialog box then click OK and Submit.Note:For a description of a field, click the information icon (i) at the top-right corner of the dialog box to display the help file.
Using a traffic analyzer at the SPAN destination, you can observe the data packets from the SPAN source EPG to verify the packet format, addresses, protocols, and other information.
ACI: Troubleshooting Endpoint Connectivity
(This is from ACI Built in Help)
- Inspect the operational status of each endpoint.The operational status will reveal any fault or misconfiguration of the endpoints. SeeInspecting the Endpoint Status .
- Inspect the status of the tunnel interface.The operational status will reveal any fault or misconfiguration of the tunnel. See Inspecting the Tunnel Interface Status.
- Perform a traceroute between the endpoint groups (EPGs).A traceroute will reveal any problems with intermediate nodes, such as spine nodes, between the endpoints. See Performing a Traceroute Between Endpoints.
- Configure an atomic counter on an endpoint.The atomic counter will confirm whether the source endpoint is transmitting packets or the destination endpoint is receiving packets, and whether the number of packets received equals the number of packets sent. See Configuring Atomic Counters.
- Inspect the contracts under each EPG.Inspect the contracts under each EPG to make sure they allow the traffic that should flow between the EPGs. As a test, you can temporarily open the contracts to allow unrestricted traffic.
- Configure a SPAN policy to forward source packets to a monitoring node.A packet analyzer on the monitoring node will reveal any packet issues such as an incorrect address or protocol. See Configuring a SPAN Session.
ACI: Configuring Atomic Counters
(This is from ACI Built in Help)
- In the menu bar, click Tenants.
- In the submenu bar, click the desired tenant.
- In the Navigation pane, expand the tenant and expand Troubleshoot Policies.
- Under Troubleshoot Policies, expand Atomic Counter Policy and choose a traffic topology.You can measure traffic between a combination of endpoints, endpoint groups, external interfaces, and IP addresses.
- Right-click the desired topology and choose Add topology Policy to open an Add Policy dialog box.
- In the Add Policy dialog box, perform the following actions:
- In the Name field, enter a name for the policy.
- choose or enter the identifying information for the traffic source.The required identifying information differs depending on the type of source (endpoint, endpoint group, external interface, or IP address).
- choose or enter the identifying information for the traffic destination.
- Optional: (Optional) In the Filters table, click the + icon to specify filtering of the traffic to be counted.In the resulting Create Atomic Counter Filter dialog box, you can specify filtering by the IP protocol number (TCP=6, for example) and by source and destination IP port numbers.
- Click Submit to save the atomic counter policy.
- In the Navigation pane, under the selected topology, choose the new atomic counter policy.The policy configuration is displayed in the Work pane.
- In the Work pane, click the Operational tab and click the Traffic subtab to view the atomic counter statistics.
ACI: Monitoring EPG Statistics
(This is from ACI Built in Help)
For detailed information about monitoring policies, see Configuring Monitoring Policies.
To collect and export statistics on one or all endpoint groups (EPGs), follow these steps:
- Create a monitoring policy.
- In the monitoring policy, configure a statistics collection policy to determine what gets collected.
- In the monitoring policy, configure a statistics export policy to determine when and to where statistics are sent.
- Apply the monitoring policy to a single EPG in an application profile or to all EPGs in an application profile.
ACI: Applying a Service Graph Template to Endpoint Groups Using the GUI
(This is from ACI Built in Help)
You must have created the following things:
- Application endpoint groups
- A service graph template
The following procedure explains how to apply a service graph template to endpoint groups:
- On the menu bar, choose Tenants > All Tenants.
- In the Work pane, double click the tenant's name.
- In the Navigation pane, choose Tenant tenant_name > L4-L7 Services > L4-L7 Service Graph Templates > template_name.
- In the Work pane, choose Actions > Apply L4-L7 Service Graph Template.You will be associating a Layer 4 to Layer 7 service graph template to your consumer and provider endpoint groups.
- In the Apply L4-L7 Service Graph Template To EPGs dialog, in the EPG Information section, complete the following fields:NameDescriptionConsumer EPG/External Network drop-down listChoose a consumer endpoint group.Provider EPG/External Network drop-down listChoose a provider endpoint group.
- In the Contract Information section, complete the following fields:NameDescriptionContract radio buttonsChoose to create a contract or choose an existing contract.Contract Name field(Only for creating a contract) Enter the name of the contract.No Filter (Allow All Traffic) check box(Only for creating a contract) Put a check in the box to allow all traffic, or remove the check from the box to filter traffic.Filter Entries(Only for filtering traffic) Click + and enter the filter information, then click Update.Existing Contract With Subjects drop-down list(Only for choosing an existing contract) Choose an existing contract.
- Click Next.
- In the Graph Template drop-down list, choose a service graph template.
- (Only for a Layer 4 to Layer 7 device) In the L4L7_device_name Information section for each Layer 4 to Layer 7 device, complete the following fields:NameDescriptionRouter Config drop-down list(Only if you chose Route Peering for the consumer type or provider type) The router configuration to use for policy-based redirect.Consumer ConnectorNameDescriptionType radio buttonsThe connector type. The type can be:
- General
- Route Peering—Enables route peering on the device.
BD drop-down list(Only if you chose General for the type) Choose or create a bridge domain for the consumer connector. The bridge domain is used for the data path traffic.L3 Ext Network drop-down list(Only if you chose Route Peering for the type) Choose a Layer 3 external (outside) network for the consumer connector.Cluster Interface drop-down listChoose or create an interface for the consumer connector.Provider ConnectorNameDescriptionType radio buttonsThe connector type. The type can be:- General
- Route Peering—Enables route peering on the device.
BD drop-down list(Only if you chose General for the type) Choose or create a bridge domain for the provider connector. The bridge domain is used for the data path traffic.L3 Ext Network drop-down list(Only if you chose Route Peering for the type) Choose a Layer 3 external (outside) network for the provider connector.Cluster Interface drop-down listChoose or create an interface for the provider connector.The Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) uses the chosen bridge domains for data path traffic between function nodes as required by the chosen service graph template. Refer to the online help for the service graph templates to learn more about how this bridge domain is used. - (Only for a copy device) In the copy_device_name Information section for each copy device, in the Cluster Interface drop-down list, choose the cluster interface that you defined for that copy device.
- (Only for a managed Layer 4 to Layer 7 device) Click Next.
- (Only for a managed Layer 4 to Layer 7 device) In the Parameters screen, in the Required Parameters tab, enter the names and values, as appropriate, for all of the required parameters.
- Click Finish.You now have an active service graph template. The APIC populates the Layer 4 to Layer 7 parameters based on the chosen function profile and colors the mandatory parameters in green if they are configured correctly.
ACI: Creating an Application Profile Using the GUI
(This is from ACI Built in Help)
- On the menu bar, choose TENANTS. In the Navigation pane, expand the tenant, right-click Application Profiles, and click Create Application Profile.
- In the Create Application Profile dialog box, in the Name field, add the application profile name (OnlineStore).
ACI: Configuring a Layer 3 Outside for Tenant Networks Using the GUI
(This is from ACI Built in Help)
- The tenant, VRF, and bridge domain are created.
- The external routed domain is created and associated to the interface.
The external routed network configured in the example can also be extended to support IPv4. Both IPv4 and IPv6 routes can be advertised to and learned from the external routed network.
- On the menu bar, click TENANTS.
- In the Navigation pane, expand the Tenant_name > Networking > External Routed Networks and perform the following actions:
- Right-click External Routed Networks and click Create Routed Outside.
- In the Create Routed Outside dialog box, in the Name field, enter a name for the routed outside.
- In the area with the routing protocol check boxes, check the desired protocol.The options available are BGP, OSPF, EIGRP. Later in the steps, this will make available, the route summarization policy in the Create External Network dialog box.
- In the VRF field, from the drop-down list, choose the appropriate VRF.
- From the External Routed Domain drop-down list, choose the appropriate external routed domain.
- Check the check box for the desired protocol.Depending on the protocol you choose, the properties that must be set.
- Expand Nodes and Interfaces Protocol Profiles.
- In the Create Node Profile dialog box, in the Name field, enter a name.
- Expand Nodes.
- In the Select Node dialog box, from the Node ID drop-down menu, choose the appropriate node ID.
- In the Router ID field, enter the router ID.
- If the Use Router ID as Loopback Address check box is checked, the Router ID is used as the Loopback Address, otherwise, expand Loopback Addresses, enter an IP address, and click Update.Note:
In the Loopback Addresses fields, create an IPv4 and/or IPv6 loopback as desired. - Click OK.
- Expand Interface Profiles, and perform the following actions:
- In the Create Interface Profile dialog box, in the Name field, enter a name for the profile.
- Expand Routed Interfaces.
- In the Select Routed Interface dialog box, from the Path drop-down list, choose the interface path.
- In the IP Address field, enter the IP address.Note:
To configure IPv6, you must enter the link-local address in the Link-local Address field in the dialog box. - Click OK.The routed interface details are displayed in the Create Interface Profile dialog box.
- Click OK.
- In the Create Node Profile dialog box, click OK.
- In the Create Routed Outside dialog box, click Next.
- In the External EPG Networks area, expand External EPG Networks.
- In the Create External Network dialog box, in the Name field, enter a name for the external network.
- Expand Subnet.
- In the Create External Network dialog box, perform the following actions:
- Expand Subnet to add another subnet.
- In the Create Subnet dialog box, in the IP Address field, enter an IP address.
- In the Scope field, check the appropriate check boxes. Click OK.Note:
- The import control policy is not enabled by default but can be enabled by the user. The import control policy is supported for BGP and OSPF, but not for EIGRP. If the user enables the import control policy for an unsupported protocol, it will be automatically ignored.
- The export control policy is supported for BGP, EIGRP, and OSPF.
- Route aggregation is also supported and the user can optionally choose route aggregation in the desired export or import direction. This feature is available for 0.0.0.0/0 and for the security option. If the import control policy is not enabled, an example of the check boxes to check are Export Subnet, Shared Security Import Subnet, and Aggregate Export. The user must choose route map and security options.
- If an explicit route control policy is configured for a Layer 3 outside, then only specific Layer 3 outside policies are supported. Explicit route control policies are not supported for aggregate routes.
- Optional: In the Route Summarization Policy field, from the drop-down list, choose an existing route summarization policy or create a new one as desired and you must check the check box for Export Route Control Subnet.
- In the Create External Network dialog box, click OK.
- Optional: In the Create Subnet dialog box, perform the following actions:
- In the IP Address field, enter the IP address and subnet.
- In the Scope field, check the appropriate check box. Click OK.
- In the Create Routed Outside dialog box, click Finish.
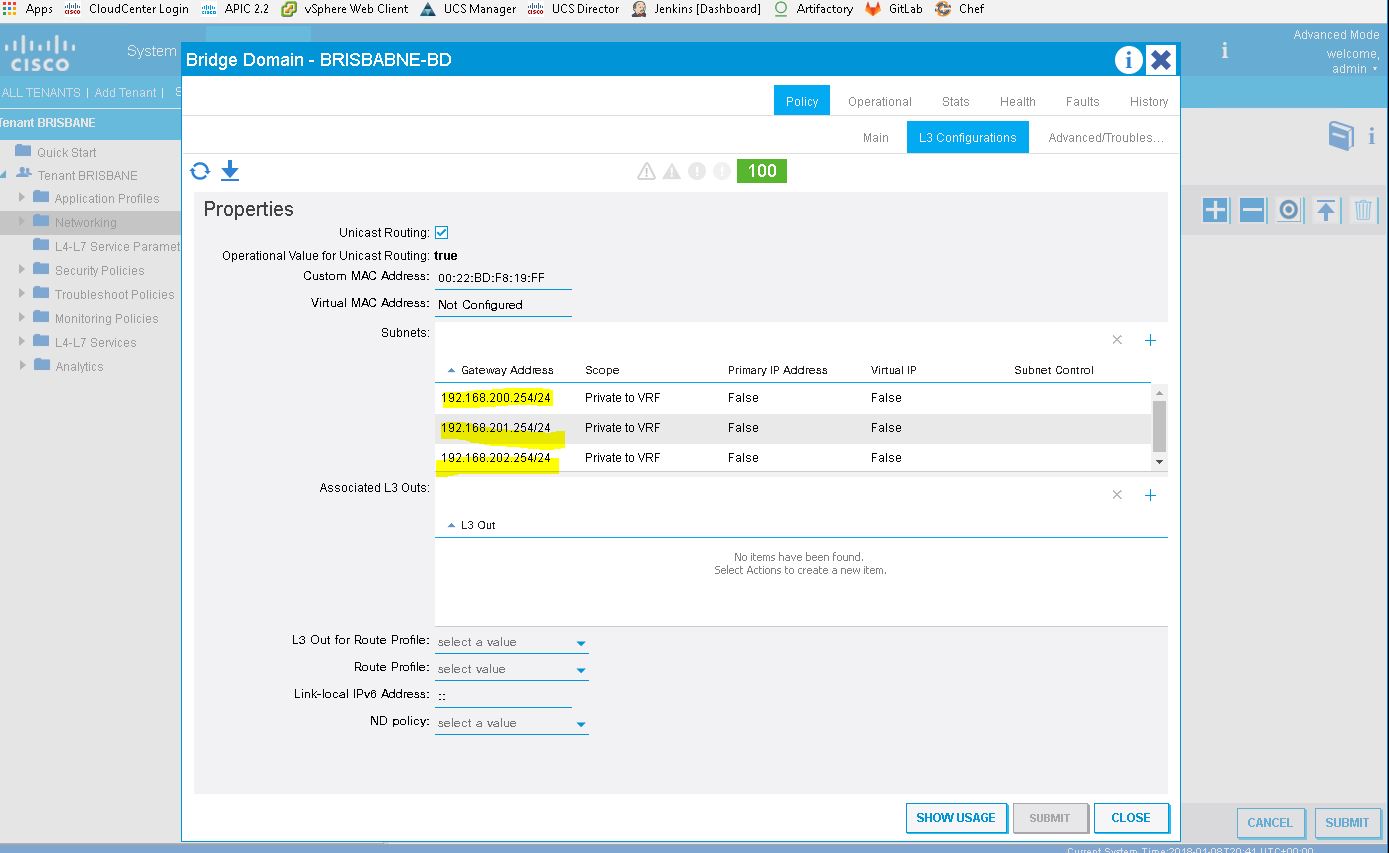
- In the Navigation pane, under Tenant_name > Networking > Bridge Domains and choose the Bridge_Domain_name.
- In the Navigation pane, choose the BD you created.Note:
If the L3 Out is static, you are not required to choose any settings.- In the Work pane, choose the L3 Configurations tab.
- In the Associated L3 Outs field, associate the desired L3 Out and click Update.
- In the L3 Out for Route Profile field, choose the desired L3 Out and click Submit.
- Note:In the Navigation pane, click Route Maps/Profiles, right-click Create Route Map, and in the Create Route Map dialog box, perform the following actions:
To set attributes for BGP, OSPF, or EIGRP communication for all routes we receive, create default-import route control profile, create the appropriate set actions and no match actions.- In the Name field, enter a name.
- In the Type field, you must click Match Routing Policy Only. Click Submit.
- Optional: To enable additional communities using the BGP protocol, right-click Set Rules for RouteMaps, click Create Set Rules for a Route Map.
- Optional: In the Create Set Rules for a Route Map dialog box,click the Add Communities field and follow the steps to assign multiple BGP communities per route prefix if desired.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
-
(This is from ACI Built in Help) In the menu bar, click Tenants . In the submenu bar, click the desired tenant. In the Navigat...
-
(This is from ACI Built in Help) The tenant, VRF, and bridge domain are created. The external routed domain is created and asso...